What is a smart meter?
A smart meter is a meter that can monitor the electricity, gas or water consumption of a building, business or household in detail and in real-time.
Based on AMR (automated meter reading) technology, smart meters transmit their data by radio waves or power line communication (PLC) to the distribution network operator.
In Europe, smart meters such are leading the transition towards more intelligent energy management. These devices, installed by network operators and utility companies in all buildings and homes, automatically collect consumption data and facilitate a range of remote operations.
When it comes to water consumption, the private operators responsible for distribution are also equipping the building.
Smart sub-metering
While the supplier's smart meter measures a building's total energy consumption for billing and distribution management, the smart sub-meter is installed inside the building to measure consumption at specific levels, providing detailed analysis. The smart submeter helps building owners or managers identify energy inefficiencies and implement targeted energy-saving measures.
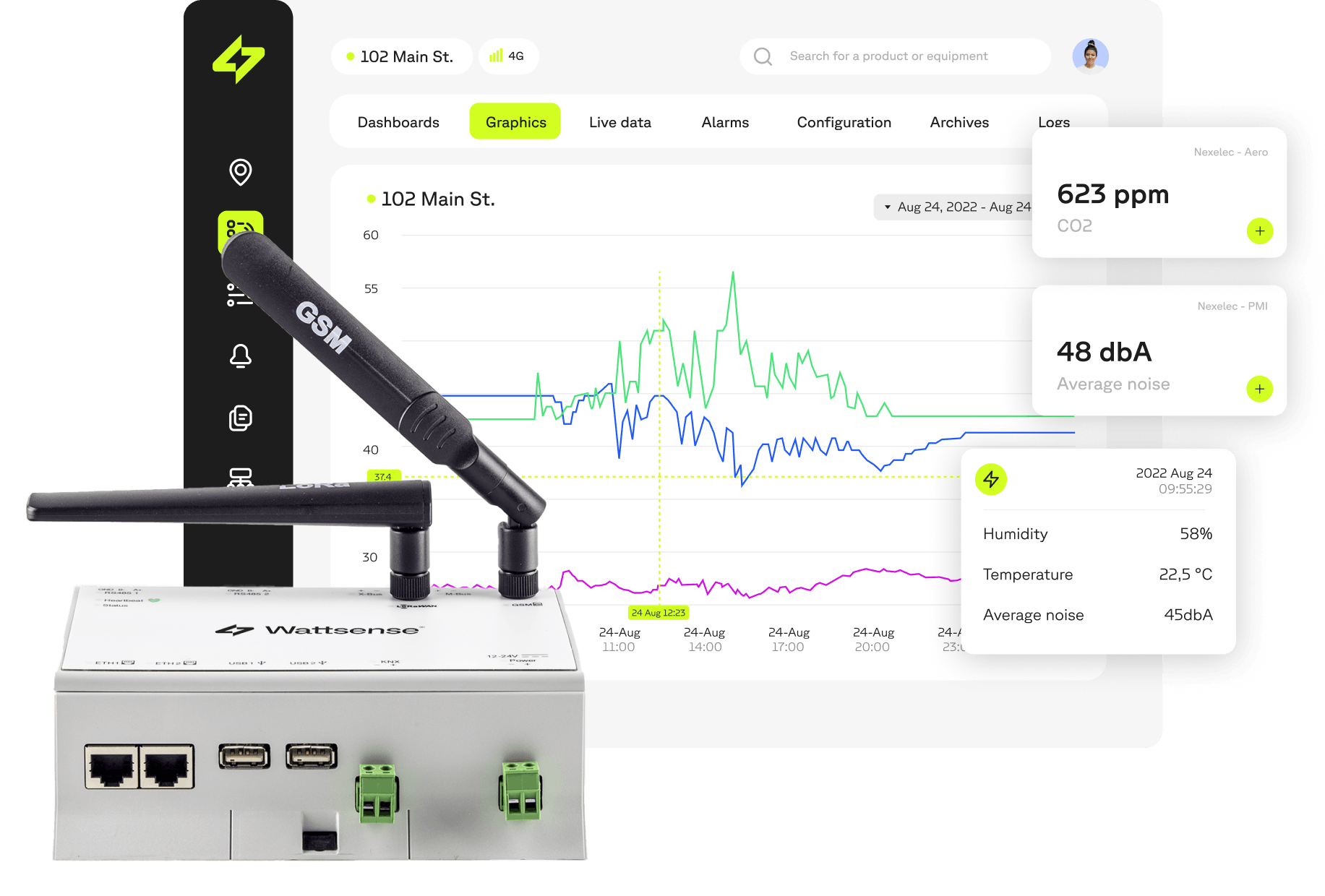
The smart meter: IoT at the service of technical building management
The smart meter embodies the successful convergence of the Internet of Things (IoT) and building automation. As an advanced device for measuring energy consumption, it takes advantage of the two-way communication capabilities of the IoT to provide real-time monitoring and efficient energy management. Thanks to its ability to transmit accurate consumption data, the smart meter enables building managers to optimise energy performance, detect anomalies and implement customised energy efficiency strategies. By integrating IoT principles into building management, smart metering represents a significant step towards smarter, more efficient and more sustainable buildings.
The integration of smart meters brings several benefits to an efficient energy management system:
- Permanent knowledge of energy consumption, enabling real-time analysis of changes.
- Based on this data, resource management strategies can be developed. In particular, this involves discussions with energy suppliers, to choose the contract best suited to the building's energy consumption and to make savings.
- Continuous monitoring makes it possible to identify where and when energy is being lost: as a result, if there are permanent 'leaks', solutions will be implemented to remedy them. If there are one-off problems, these will be immediately visible in the monitoring, and rapid intervention will limit the effects.
Combined with high-performance supervision systems such as BMS or EMS, a whole system of resource-efficient management and predictive maintenance can be created. By centralising all the data collected by sensors and communicating meters, it becomes easy to control all the energy parameters of a building. This is what Wattsense is offering with its universal connectivity solution.
Unlock Building Performance
Our connectivity solution centralises data from smart meters and other technical systems in a building for real-time visualisation and improved control. All without major works, equipment changes or additional complexity.